4.1 個人的屬性
與個人相關聯的日期
個人的頭銜
性別
出生地
死亡地
國別
居住地
機構
地址
個人的語言
活動領域
專業/職業
傳記/歷史
與個人相關聯的其他信息
4.2 家族的屬性
家族的類型
家族的日期
與家族相關聯的地點
活動領域
家族歷史
4.3 團體的屬性
與團體相關聯的地點
與團體相關聯的日期
團體的語言
地點
活動領域
歷史
其他與團體相關聯的信息
4.4 作品的屬性
作品的形式
作品的日期
演出媒體
作品的主題
編號標識
調名
作品的原產地
歷史
其他區分特徵
4.5 內容表達的屬性
內容表達的形式
內容表達的日期
內容表達的演出媒體
內容表達的語言
技術
其他區分特徵
4.6 載體表現的屬性
版本/發行標識
出版/發行地
出版者/發行者
出版/發行的日期
載體形式
編號
4.7 單件的屬性
單件的地點
單件的保管歷史
單件的直接獲取來源
4.8 概念的屬性
4.9 實物的屬性
4.10 事件的屬性
4.11 地點的屬性
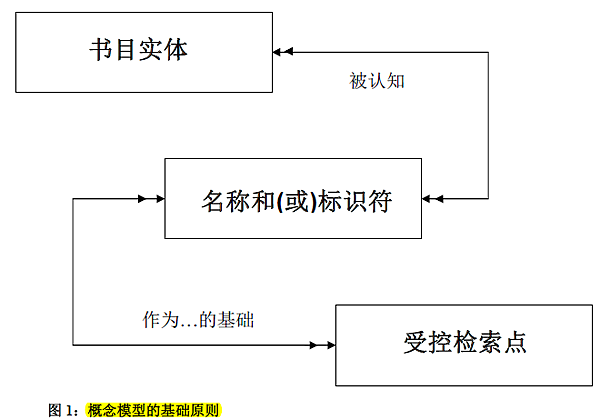
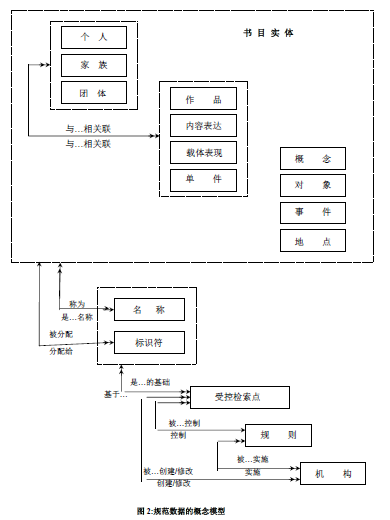
4.12 名稱的屬性
名稱的類型
名稱字符串
使用範圍
使用的日期
名稱的語言
名稱的文字
名稱的字母譯音系統
4.13 標識符的屬性
標識符的類型
4.14 受控檢索點的屬性
受控檢索點的類型
受控檢索點的狀態
受控檢索點的指定用法
未區分檢索點
基本檢索點的語言
編目的語言
基本檢索點的文字
編目的文字
基本檢索點的字母譯音系統
編目的字母譯音系統
受控檢索點的參考源
基本檢索點
附加成分
4.15 規則的屬性
規則的引用
規則標識符
4.16 機構的屬性
機構的名稱
機構標識符
機構的地點